Sycamore trees are truly magnificent. They stand tall and strong across the United States, with a beauty that catches the eye. This article is your guide to understanding what makes sycamore trees stand out. We'll cover the basics: the different types of sycamore trees, how to recognize them by their leaves, bark, and flowers, and the common issues they face.
What is Special About a Sycamore Tree?
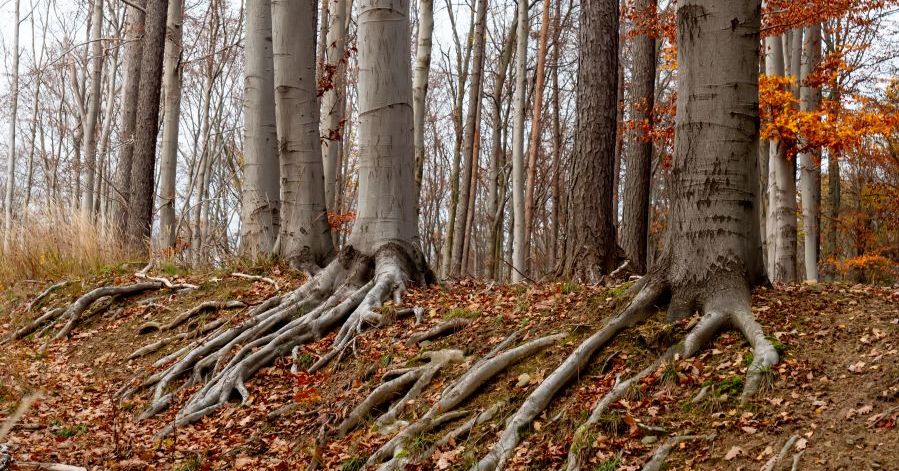
Sycamore trees (Platanus occidentalis) are renowned for their grandeur and resilience. Native to North America, these trees are often found along riverbanks and in floodplains, where their sturdy roots help prevent erosion. One of the most striking features of Sycamores is their mottled bark, which peels away in patches to reveal a creamy white inner bark, adding visual interest to landscapes year-round.
These trees are also valued for their large, palmate leaves, providing ample shade during hot summer. The Sycamore's adaptability to various soil types and climates makes it an ideal choice for landscaping and urban forestry projects.
Types of Sycamore Trees
Sycamores encompass several species, each with unique characteristics and geographical distribution. Let's explore some of the most notable types of sycamore trees:
- American Sycamore (Platanus occidentalis): Native to North America, the American Sycamore is one of the largest hardwood trees on the continent. It features distinctive mottled bark and broad, lobed leaves that turn a vibrant yellow in the fall.
- California Sycamore (Platanus racemosa): Endemic to California and parts of Mexico, the California sycamore is prized for its attractive peeling bark and lush foliage. Its leaves appear similar to the American Sycamore but may have a slightly different shape.
- Arizona Sycamore (Platanus wrightii): Found in the southwestern United States and northern Mexico, the Arizona sycamore is well-adapted to hot, arid climates. It has deeply lobed leaves and smooth, light-colored bark that exfoliates in large patches.
- Sycamore Maple (Acer pseudoplatanus): Despite its name, it is not a true sycamore but a maple tree species native to Europe and western Asia. It has palmately lobed leaves similar to sycamore trees but belongs to a different genus.
- Mexican Sycamore (Platanus mexicana): Indigenous to Mexico, the Mexican Sycamore is prized for its rapid growth rate and tolerance to heat and drought. It has large, deeply lobed leaves and smooth, peeling bark.
- Oriental Plane Tree (Platanus orientalis): Also known as the Old World sycamore, the Oriental plane tree is native to southeastern Europe and western Asia. It has similar characteristics to the American Sycamore but may have subtle differences in leaf shape and bark texture.
Identifying Sycamore Trees in the Landscape
Spotting a sycamore tree in the wild or urban settings can be a rewarding experience, especially once you know what to look for. Here are some tips for identifying sycamore trees in their natural habitat:
- Look for Large, Broad-Leaved Trees: Sycamores are typically large trees with broad, spreading canopies. Keep an eye out for trees with sizable leaves and thick trunks.
- Examine the Bark: Sycamores are known for their distinctive bark, which often peels away in irregular patches to reveal lighter-colored inner bark. This mottled appearance is a telltale sign of a sycamore tree.
- Observe Leaf Shape and Texture: Take a close look at the leaves of the tree. If they are extensive, broad, and palmately lobed, chances are you've found a sycamore. Pay attention to the texture of the leaves, as sycamore leaves are typically smooth and leathery.
- Note the Surroundings: Sycamores are often found in riparian zones near rivers, streams, and wetlands, where they thrive in moist, fertile soil. Keep an eye out for sycamores in these types of environments.
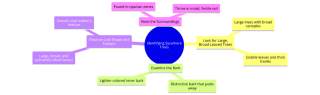
Sycamore Leaf Identification
One of the most distinctive features of sycamore trees is their leaves. Sycamore leaves are large, palmately lobed, and have a unique shape that sets them apart from other tree species. Let's take a closer look at how to identify sycamore leaves:
- Size: Sycamore leaves are typically large, measuring 4 to 10 inches wide. Their substantial size makes them easy to spot, especially in the canopy of mature trees.
- Shape: Sycamore leaves have a broad palate shape, resembling an open hand with several lobes radiating from a central point. The number of lobes can vary, but most sycamore leaves have five distinct lobes.
- Texture: The surface of sycamore leaves is smooth and leathery, with a slightly glossy appearance. The underside of the leaves is often paler in color and may have a fuzzy texture.
- Color: Sycamore leaves are typically bright green in the spring and summer, gradually turning yellow or brown in the fall before dropping from the tree.

Sycamore Tree Bark
The bark of a Sycamore tree is perhaps its most recognizable feature. Initially, it appears dark brown and rough. Still, as the tree matures, the bark peels away in irregular patches, exposing the smooth, whitish inner bark beneath. This shedding of bark gives the tree a distinctive camouflage-like appearance.
Sycamore Tree Flowers
Sycamore trees produce small, round, greenish-yellow flowers in the spring, which develop into spherical seed balls that hang from the branches. These seed balls contain numerous tiny seeds equipped with feathery appendages aiding wind dispersal.
Sycamore Tree Pests And Diseases
While Sycamore trees are relatively resilient, they are susceptible to certain pests and diseases that threaten their health.
Sycamore Anthracnose
Anthracnose is a fungal disease affecting many tree species, including Sycamores. It causes dark leaf lesions, leading to defoliation and tree weakening. Proper pruning and sanitation practices can help manage anthracnose outbreaks.
Sycamore Lace Bug
The Sycamore lace bug is a tiny insect that feeds on the undersides of Sycamore leaves, causing them to become stippled or discolored. Severe infestations can weaken the tree and lead to premature leaf drop. Insecticidal soap or horticultural oil can be effective in controlling lace bug populations.
Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease that affects many ornamental trees, including Sycamores. It appears as a white powdery coating on the leaves and can inhibit photosynthesis if left untreated. Fungicidal sprays or cultural practices such as improving air circulation can help prevent powdery mildew.
Contact Strobert Tree Services - Leaders in Tree Care in Delaware, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey
If you have sycamore trees on your property and are concerned about their health or need assistance with maintenance, Strobert Tree Services is here to help. With years of experience and a team of skilled arborists, we specialize in providing comprehensive tree care services tailored to each client's unique needs.
Whether you need pruning, disease management, or emergency tree removal, you can count on us to deliver prompt, professional service with a focus on quality and safety. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and experience the difference that our expertise and dedication can make for your trees.